How To Start Learning SEO For Free

SEO stands for “search engine optimization.” In simple terms, SEO means the process of improving your website to increase its visibility in Google, Microsoft Bing, and other search engines whenever people search for:
- Products you sell.
- Services you provide.
- Information on topics in which you have deep expertise and/or experience.
The better visibility your pages have in search results, the more likely you are to be found and clicked on. Ultimately, the goal of search engine optimization is to help attract website visitors who will become customers, clients or an audience that keeps coming back.
When embarking on a new endeavor, such as delving into the intricacies of search engine optimization (SEO), it’s common to feel overwhelmed. Yet, mastering SEO can significantly enhance your business prospects.
Regrettably, the SEO landscape is rife with mediocre service providers who promise the world but fail to deliver. This is why coaching in SEO for business owners and website managers often proves to be the most reliable path to success. Armed with the right guidance, you can optimize your website effectively without relying on costly yet unreliable third-party services. By learning SEO yourself, you can sidestep the risk of being misled by purported experts with questionable credentials.
With this in consideration, let’s explore the 10 steps to kickstart your journey into the realm of SEO learning.
1. Understanding Your Objectives:
Each company harbors distinct marketing objectives. However, ultimately, the aim for everyone is to enhance revenue through online avenues, which aligns with the fundamental purpose of SEO.
By aligning your website with optimal SEO practices, you enhance the likelihood of securing high rankings in SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages). Achieving a top position within your niche translates to a substantial increase in traffic.
Organic SEO primarily focuses on amplifying traffic. The rationale is straightforward: a surge in website visitors results in more qualified leads, thus bolstering the likelihood of conversions.
But how exactly do these SERP rankings function? What criteria does Google employ to determine which websites merit top positions in searches?
Search engines like Google utilize “bots” or “spiders” — digital crawlers that traverse the vast expanse of the internet, indexing website content and subsequently ranking them. Consequently, SEO constitutes a concerted effort to appease Google’s algorithm, thereby enhancing the likelihood of your website securing a higher rank through various optimization strategies.
2. Master the Basics of SEO
If you’re new to SEO fundamentals, this is your starting point. It’s crucial to comprehend how search engines operate and grasp the four primary facets of SEO. Let’s delve into these essentials.
SEO Basics
Having an understanding of foundational SEO vocabulary is important. Let’s dive into a few key words to know:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): The tactics you use to optimize your website to ensure you provide the high-quality information searchers look for and rank higher in search results for specific keywords so people can find your content.
- On-page SEO: Any optimizations you’d make within your website to improve search rankings, like the keywords used in your content or back-end elements like site structure.
- Off-page SEO: Any actions you take to improve your search engine rankings outside your website, like backlinks from other websites or guest blogging.
- Link building: Getting links to your website from other high-quality websites to build authority and credibility.
- SERPs: SERPs stands for Search Engine Result Pages, and it’s the results page after someone conducts a search.
- White-hat SEO: Optimization tactics that align with accepted and recognized best practices.
- Black-hat SEO: Optimization tactics that manipulate search engine algorithms to rank websites higher in SERPs. These tactics are often unethical.
- E-E-A-T: E-E-A-T stands for experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trust. It’s part of Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines and one of the factors Google uses to determine a page’s relevance and authority.
- Keyword: Words or phrases users type into a search engine to find content related to their search. As an SEO, you include relevant keywords in your content that align with search intent so your site appears in related searches.
- Keyword Research: The process of finding keywords people enter into search results related to your business to help you inform the words to use in your website pages and content.
- Organic/Organic results: Any results in SERP that are unpaid and that appear because of a page’s relevance to the search query.
- Organic traffic: Organic traffic is traffic that comes from organic results.
- Rank/page ranking: Where your site falls in SERPs for a specific keyword.
- Ranking factor: A ranking factor is an element that impacts where your site may fall in search results, like your page authority.
- Search intent: Search intent is why a user conducts a search.
3. Understanding the Various Types of SEO
The primary types of SEO encompass:
1. On-page SEO: This involves optimizing specific web pages to enhance their ranking. Tactics may include content optimization, title tag optimization, and internal linking.
2. Off-page SEO: Refers to SEO activities conducted outside of your website. Strategies encompass link building, content syndication, and social media management.
3. Technical SEO: Focuses on improving the technical aspects of your website to enhance both user experience and search engine performance. Tactics include optimizing page speed and refining site architecture.
Moreover, SEO tactics are tailored to specific content formats:
– Image SEO: Involves optimizing images to achieve better rankings in standard search results and image search results.
– Video SEO: Aims to optimize videos for improved rankings in regular search results, image results, video results, and on platforms like YouTube.
Furthermore, there are specialized SEO disciplines catering to specific types of businesses or websites, such as:
– Local SEO: Tactics designed to elevate the ranking of local businesses in local search results.
– International SEO: Strategies for websites serving multiple languages and geographic locations.
– Ecommerce SEO: Techniques tailored for online stores to enhance visibility and drive sales.
– SaaS SEO: Tactics aimed at optimizing the online presence of software as a service (SaaS) businesses.
– Small Business SEO: Strategies tailored to the unique needs and constraints of small businesses.
– B2B SEO: Tactics devised for business-to-business (B2B) brands to enhance visibility and attract relevant leads.
4. Understand SEO Ranking Factors
SEO ranking factors are things that affect your website’s and individual pages’ performance in search engine results.
According to our ranking factors research, the most important Google ranking factor is text relevance. Meaning how relevant your page’s content is to the user’s query.
Google also considers things like:
- How fast your page loads
- The number of other sites link to your website
- Whether your page uses the secure HTTPS protocol
5. Enroll in Free Courses:
If you prefer structured learning environments, consider taking advantage of free SEO courses to enhance your skills. Many courses also offer certificates upon completion. Here are some reputable options:
– HubSpot Academy SEO Training Certification (free): Ideal for beginners
– Google Analytics Academy (free): Offers beginner and advanced learning paths
– MOZ Academy (paid): Provides courses for various skill levels
– Semrush Academy (free): Offers courses suitable for different proficiency levels
6. Stay Informed About Trends
SEO is a dynamic field, with algorithms frequently updated and new trends emerging regularly. For instance, Google recently incorporated an “E for Experience” into its existing E-A-T guidelines to ensure content is valuable, pertinent, and authored by experienced individuals in the respective subject matter.
This adjustment becomes increasingly vital as AI-generated content gains popularity, as human experience serves as a critical distinguishing factor from computer-generated content.
Hence, staying abreast of trends is paramount to becoming an SEO expert. It enables you to adapt swiftly to significant industry shifts. HubSpot Blog covers SEO landscape changes, while Google maintains a comprehensive list of major updates affecting SEO success.
7. Understanding Search Engine Operations
Search engines function by discovering content and archiving it within a vast database referred to as an index. Think of this index as a digital library storing web pages instead of physical books. When you initiate a search, the search engine retrieves matching results from this index. Subsequently, intricate algorithms, known as search algorithms, rank these results.
Therefore, when you conduct a search on Google, you’re not scouring the entire web; you’re specifically querying the pages within Google’s index.
This distinction holds a pivotal significance:
If your content isn’t indexed by Google, it won’t appear in their search results.
Google compiles its index from two primary sources:
1. Sitemaps: A sitemap is a file that enumerates all the vital pages on your website that you desire search engines to index. You can submit your sitemap to Google, notifying it of the existence of your pages.
2. Links from Established Webpages: Google’s index comprises billions of pages. If your website obtains a link from one of these pages, Google can “follow” the link to discover and index your page.
It’s noteworthy that established webpages aren’t exclusively external sites. Google can identify new pages within your site by tracing links from established pages on your website.
For instance, suppose Google has already indexed your blog homepage. In that case, by adding an internal link to a new blog post from there, Google can “follow” that link and index the post.
8. Developing Key SEO Skills
Mastering SEO entails honing a variety of skills across multiple disciplines. Below are some of the most crucial skills essential for SEO success:
1. Keyword Research
Keyword research involves identifying search terms (keywords) that resonate with relevant audiences and are likely to drive traffic to your website. A robust keyword research tool aids in analyzing:
– Search volume: The average monthly search volume for a keyword.
– Keyword difficulty: An assessment of the competitiveness of ranking for a particular keyword.
– Search intent: Understanding the underlying motivation behind a user’s search query, also known as keyword intent.
Tip: Utilize keyword research tools to uncover valuable insights into user search behavior and optimize your content accordingly.
Undoubtedly, achieving the top spot in search results for every conceivable query is unrealistic. Instead, the focus is on securing high rankings for specific keywords—terms individuals input when conducting searches on Google.
As a business owner, identifying the keywords relevant to your company or competitors is crucial. The objective is to surpass competitors in SERPs, thereby capturing the lion’s share of traffic that would otherwise gravitate towards them.
The significance of keyword research in SEO becomes evident in this context. By selecting keywords that harmonize naturally with your business and competing for them strategically, you expand your online visibility to a broader audience.
Diving deeper, it’s essential to understand the distinction between two types of keywords prevalent in search engines: long-tail and short-tail. Short-tail keywords typically comprise only a couple of words, whereas long-tail keywords consist of three or more.
Typically, long-tail keywords yield more specific results. For instance, entering “where to stream The Boys” delivers precise information about the TV show, whereas a broader term like “the boys” may yield generic information or unrelated content.
In the realm of keyword research, SEO professionals rely on an array of tools to gather essential data necessary for making informed decisions.
Keyword research serves as the foundational step in a comprehensive SEO strategy. Armed with the knowledge of target keywords, businesses can seamlessly incorporate them into titles, URLs, meta descriptions, and content, optimizing their online presence.
2. SERP Analysis
Assessing the search engine results page (SERP) and results for a given keyword is called SERP analysis.
It allows you to identify SEO ranking opportunities. And work out what you need to do to secure them.
For example, the SERP for “chocolate cake” is dominated by recipes on popular sites that search engines see as reputable. This means that other types of content and lesser-known sites might struggle to rank here.
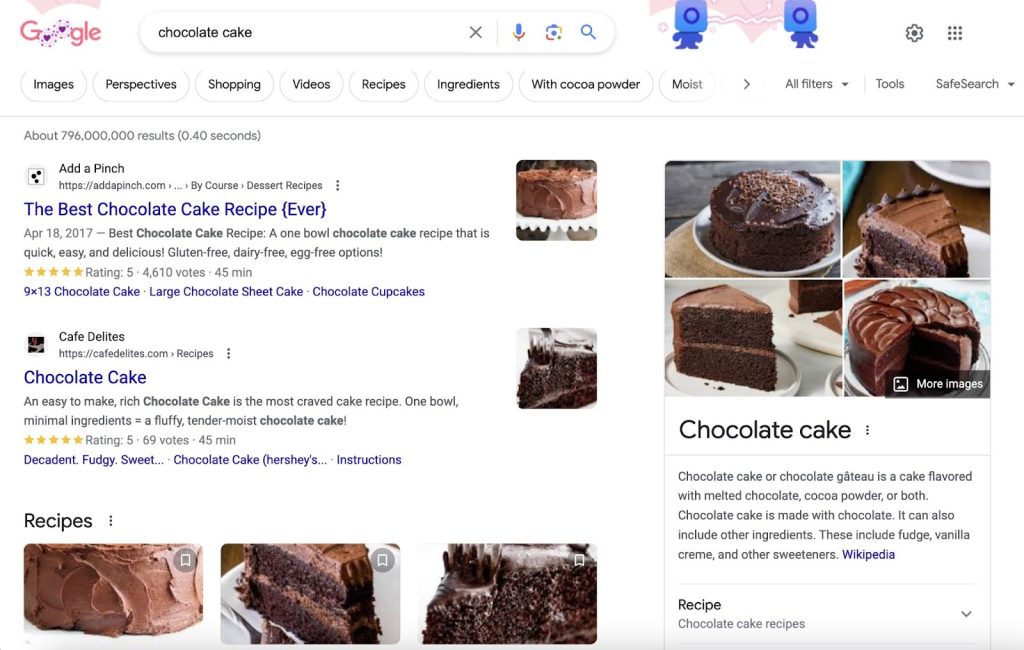
You’ll also notice various SERP features (non-standard search results). Such as rich snippets with star ratings.
If you were writing a chocolate cake recipe, you could optimize for these elements. With the goal of getting more visibility and clicks.
3. Content Creation
Content creation is an important part of SEO because it gives search engines something to evaluate and rank.
For the best results, you’ll need to:
- Come up with relevant content ideas or blog ideas
- Take advantage of content creation tools
- Create quality content that’s tailored to your target audience
- Distribute your content across various channels
Generally, Google wants to rank unique content that demonstrates Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). Because it wants to provide helpful and reliable results to users.
This means your content should be accurate, comprehensive, and relevant to your brand.
4. On-Page Optimization
On-Page Optimization entails enhancing both technical and content aspects of your webpages to make them more user-friendly and relevant to your target keywords. This process aims to improve your search engine ranking and attract increased organic traffic to your site.
Key elements of on-page optimization include:
- Title tags: These clickable headlines, visible in search results, should incorporate your primary keyword and a compelling value proposition to entice users to click through to your page.
- Meta descriptions: Brief snippets of text appearing below headlines in search results, providing a concise summary of your page content along with a call to action to encourage user clicks.
- Headers: Subheadings structuring your content and enhancing readability. Utilize relevant keywords and maintain a logical hierarchy (H1, H2, H3, etc.).
- Content: The main body of your page, delivering valuable and engaging information to your audience. Ensure thorough coverage of your topic, addressing searcher queries, and utilizing natural language alongside variations of your keywords.
- Images: Visual elements complementing your page content and appealing to your audience. Assign descriptive alt text to images, illustrating their content, and include relevant keywords when appropriate.
- Internal links: Links interconnecting your pages, facilitating site navigation for users. Employ descriptive anchor text indicating the linked page’s content.
To perform on-page optimization effectively, utilize tools capable of analyzing your pages at scale.
For example, SemRush On Page SEO Checker pinpoints weaknesses and provides suggestions on how to improve pages across your site.
5.Technical SEO:
Technical SEO involves enhancing the technical infrastructure of your website to ensure efficient crawling and indexing by search engines.
Key components of technical SEO include:
- XML sitemap: This file enumerates all the pages you wish search engines to index, facilitating their discovery and navigation through your website.
- Robots.txt file: By defining which pages search engines should crawl or avoid, this file directs their behavior and ensures efficient indexing of your site’s content.
- Meta robots tags: These HTML tags provide instructions to search engines regarding the crawling, indexing, and presentation of specific pages, thereby influencing their visibility in search results.
- Structured data: Incorporating structured data markup aids search engines in comprehending and interpreting your content more effectively, potentially enhancing its visibility and relevance in search results.
6. Link Building:
Link building refers to a series of strategies focused on acquiring links from pertinent and reputable websites.
This practice holds significance as search engines often interpret these inbound links (backlinks) as signals of a website’s credibility and excellence.
The concept is straightforward:
When numerous authoritative websites link to a specific page, that page is perceived as authoritative as well. Hence, link building has long been integral to SEO endeavors.
7. Website Architecture
Website architecture is the hierarchical structure of your webpages and how they’re linked together. It affects both the user experience and your SEO performance.
Here’s a visual example of website structure:
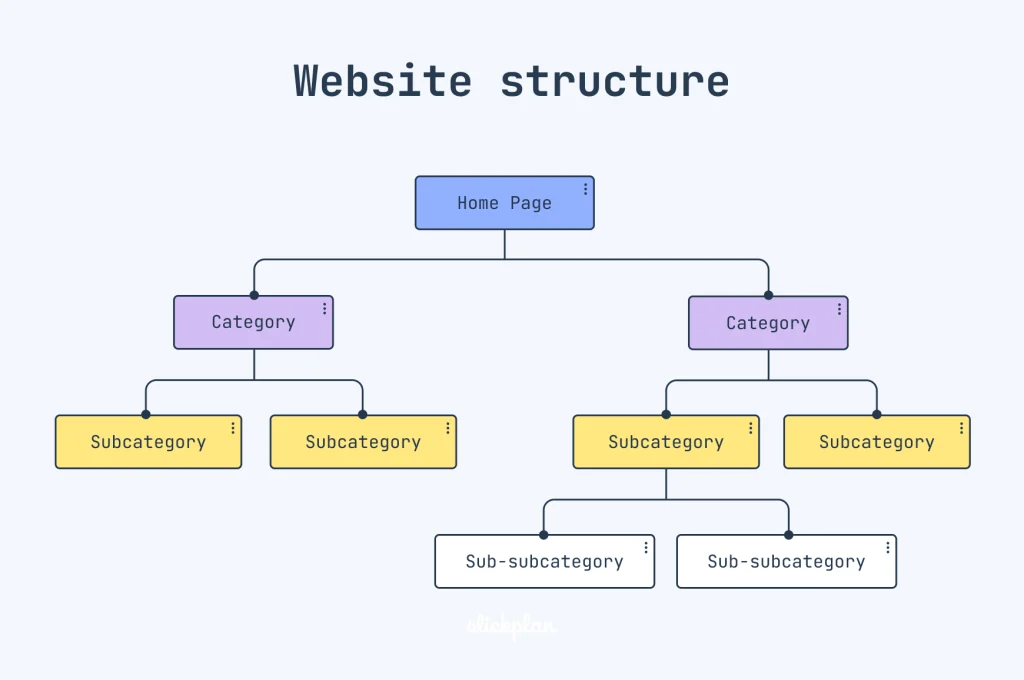
A good website architecture should:
- Help users easily find the information they need and navigate your site smoothly
- Help search engines crawl and index your site efficiently and understand the relationships between your pages
- Distribute your page authority evenly and boost your topical authority for your target keywords
8. SEO Performance Monitoring
Being able to track and analyze SEO results is a vital skill. Because it tells you what strategies work best for your business.
It’s a good idea to monitor SEO key performance indicators (KPIs) like:
- Keyword rankings
- Organic traffic
- Organic conversions
9. Utilize SEO Tools:
Given the vast expanse of the internet, handling essential SEO tasks manually would be daunting. This is where SEO tools step in to streamline processes, saving considerable time and effort while delivering desired results promptly.
Here’s a curated list of recommended tools:
1. Google’s Search Console: Assists in measuring site traffic and rectifying SEO performance issues.
2. Google Analytics: Offers insights into key metrics essential for understanding SEO efforts, including organic vs. non-organic traffic.
3 . HubSpot’s SEO Marketing Software: Provides SEO recommendations for site improvement, content optimization, and ROI measurement.
4. Website Grader: Scores your site based on factors such as mobile-friendliness and SEO optimization.
5. Check Page Rank: Monitors your website’s rank and domain authority.
6. Ahrefs: Facilitates keyword research and provides crucial statistics like search volume and CTR.
7. Seobility: Analyzes technical aspects of your site to identify and resolve on-page SEO issues.
8. Jasper: An AI writing assistant that aids in crafting SEO-optimized blog posts with target keywords.
Once you’ve embarked on your SEO learning journey and feel prepared to dive in.
10. Stay Updated with SEO Trends
While the core principles of SEO remain relatively stable, the landscape continually evolves with incremental changes. Google updates its algorithms frequently, search engines adapt their handling of technical SEO elements, and innovative strategies emerge from industry experts.
Therefore, while it’s unnecessary to immerse yourself in SEO news constantly, it’s crucial to stay informed. Here are some effective methods to keep your finger on the pulse:
- Attend SEO Conferences and Meetups
Participate in industry conferences like BrightonSEO, which attract thousands of professionals. Additionally, explore smaller local meetups listed on platforms like meetup.com, offering valuable insights and networking opportunities. - Listen to SEO Podcasts
Podcasts feature interviews with experienced SEO practitioners, offering valuable insights and discussions about successful tactics. Consider subscribing to podcasts like the Authority Hacker podcast to stay updated while on the move. - Join SEO Facebook Groups
Engage with active communities of SEO professionals on Facebook, where members share knowledge and offer advice. Explore groups like Ahrefs Insider for lively discussions and support. - Join SEO Slack Communities
Participate in Slack communities dedicated to SEO, offering a platform for real-time discussions and collaboration. Some communities are free, while others may require a subscription. - Read SEO Blogs
Regularly follow reputable SEO blogs for unique insights, case studies, and industry updates. Websites like the one you’re currently reading provide valuable resources for staying informed. - Watch SEO YouTube Videos
Subscribe to YouTube channels focused on SEO to access informative videos covering various topics and strategies. - Monitor Official Sources
Stay updated on Google’s algorithm updates and announcements through the Search Console Blog and weekly office hours hangouts on its YouTube channel. Follow Google search representatives like John Mueller and Gary Illyes on Twitter for additional insights. - Read SEO News Websites
Stay informed with daily updates from reliable SEO news sources like Search Engine Roundtable, Search Engine Land, and Search Engine Journal, covering the latest developments in the search marketing industry.












